

Tapentadol (Nucynta)
Tapentadol is the strong pain medicine that contains an opioid that is used to manage pain severe enough to require daily around-the-clock, long-term treatment with an opioid, when other pain treatments such as non-opioid pain medicines or immediate-release opioid medicines do not treat your pain well enough or you cannot tolerate them.
Tapentadol also used to manage pain from damaged nerves (neuropathic pain) that happens with diabetes and is severe enough to require daily around-the-clock, long-term treatment with an opioid, when other pain treatments such as non-opioid pain medicines do not treat your pain well enough or you cannot tolerate them.
A long-acting (extended-release) opioid pain medicine that can put you at risk for overdose and death. Even if you take your dose correctly as prescribed you are at risk for opioid addiction, abuse, and misuse. Tapentadol not used to treat pain that is not around-the-clock pain. Tapentadol brand names: Nucynta, Palexia, Yantil, Tapenta, Tapal. Although the clinical relevance is unclear, preclinical studies have shown that tapentadol is a opioid receptor agonist and a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor.

What kind of pain Tapentadol treat
Two main types of pathophysiology are often the cause for pain in the majority of patients, nociceptive pain and neuropathic pain. Common ypes of chronic pain, including diabetic peripheral neuropathy and conditions that originate or are common to the low back. Patients with chronic pain conditions may have both a neuropathic and a nociceptive component.
- Diabetic peripheral neuropathy. A complication of diabetes in which high blood glucose may damage the tiny blood vessels carrying oxygen and nutrients to the small nerves in the hands and feet.
- Intervertebral disc disease. A condition typically caused by aging in which discs in the vertebral column deteriorate or herniate, causing them to lose fluid, elasticity, and shock-absorbing capabilities.
- Radiculopathy. Nerve damage typically caused by inflammation or impingement of a nerve root, causing weakness or pain radiating the length of the nerve.
- Arthritis. There are several forms of arthritis of the spine (known altogether as spondyloarthropathies).
- Osteoarthritis. Occurs when the cartilage that protects the bones of the spinal area breaks down, causing bones to rub together, which leads to spurs that press against nerves.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis. Occurs when the immune system attacks soft tissue surrounding the joints of the spine, which can place pressure on the spinal cord or spinal nerve roots.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis. An inflammatory disease in which the ligaments and bones of the spine fuse together, resulting in a stiff, fused, painful spine.
- Spondylolisthesis. A condition in which a lower vertebra slides out of place on top of the vertebra below it, commonly between L4 and L5, causing low back pain.
Tapentadol effectiveness
Despite the availability of new therapies, neuropathic pain continues to pose challenges to patients and practitioners alike. It is often chronic in nature and, in a substantial number of patients, is relieved only by medication such as Tapentadol. The mainstay of treatment for most types of neuropathic pain consists of antidepressants, anticonvulsants, topical anesthetics, and opioid analgesics. Only a handful, however, have been FDA approved. In order to achieve clinically meaningful pain relief, patients commonly require Tapentadol. Treatment is often complicated by coexisting health conditions, and current guidelines recommend a highly individualized approach to management. Practitioners can play a key role in helping patients optimize drug therapy and minimize the consequences.
In USA chronic pain is a challenging, widespread problem. Pain management and primary care physicians are often faced with nonmalignant pain syndromes and with those suffering from neuropathic pain. While potent opioids are associated with significant adverse events, nonopioid analgesics may not be sufficient to achieve adequate analgesia among patients with moderate to severe chronic pain.
Dosing information
Individualize therapy taking into consideration severity of pain, response to therapy, prior analgesic treatment experience, and risk factors for addiction, abuse, and misuse. For the management of acute pain severe enough to require an opioid analgesic and for which alternative treatments are inadequate. Extended Release Nucynta Tablets, as the name would suggest, lasts longer than the immediate release counterpart.
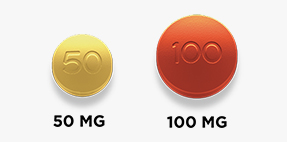
Usual Adult Dose for Pain:
Tapentadol comes as a tablet and an extended-release (long acting) tablet to take by mouth. The tablets are usually taken with or without food as needed. Initial dose: 50 mg to 100 mg orally every 4 to 6 hours as needed for pain. A second dose may be administered as soon as 1 hour after the first dose if needed. Subsequent dosing: 50 mg, 75 mg, or 100 mg orally every 4 to 6 hours. Adjust dosing to maintain adequate analgesia with acceptable tolerability. Maximum daily dose: 700 mg.
Post-C-Section Pain
What type of pain relief will doctor choose if expectant mom need to have a C-section? While opioids can control pain, a combination of other painkillers could offer similar relief with fewer side effects and no risk of addiction. A big concern anytime opioids are used is the potential for addiction. As many as one in three people given a long-term prescription for opioids in primary care has reported struggling with addiction, according to the USA Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Opioids do not need to be routinely prescribed for every woman. Pain control can be done effectively with Motrin and Tylenol. For those who do need opioids, it's not need to give out as much. But for some patients, saving opioids are really needed.
Benefits
In the United States, there are millions people living with diabetes and, over time, they can develop a type of nerve damage called neuropathy. Approximately 80 percent of people with diabetes have some form of neuropathy. The most common type causes pain or loss of feeling in the toes, feet, legs, hands, and arms. It is estimated that many patients on current treatments experience considerable pain. Tapentadol has efficacy to reduce diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain compared to placebo. The data also provide evidence of long-term safety and tolerability of this medicine.
Opioids are frequently used to treat chronic pain, and adverse effects often restrict their long term benefits. Tapentadol is an opioid and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor, which may cause a lower incidence and severity of adverse effects compared to other strong opioids.
An important patient consideration is cost. Tapentadol is a new drug, being marketed as NUCYNTA. When prescribing it, caution must be taken to weigh the risks and benefits. Studies have shown that when using tapentadol, reduced adverse effects as compared to other opioids offset the cost, and that patients are more likely to continue their regimen of tapentadol without switching to another opioid.
Tapentadol may be administered orally with or without food as circumstances allow, and the patient will generally not notice any change in the efficacy and duration of analgesic effects if the drug is not consistently administered in fasting or fed states, patients will receive the same benefits from their dose regardless of what and when they last ate.
Where to buy Tapentadol?
Tapentadol is a pain medication that is relatively new to the market. It was initially approved by the FDA as an immediate release formulation and an extended release version was approved later. Buying Tapentadol online is not only cheaper, it’s also less of a hassle, as the drug is delivered to your home. It’s however important to note that you should buy Tapentadol only from verified online pharmacies. The online pharmacy which have a good reputation would be the right choice for buying this medicine.